Google AMP is an open-source project that allows developers to create stripped-down, faster versions of websites. It helps pages load faster by removing or reducing slow-loading elements like JavaScript and minimizing style recalculations. Accelerated mobile pages are also displayed more quickly in Google’s Top Stories carousel on mobile search results. With speed being an important SEO ranking factor, many website owners have been wondering about the relevance of Google AMP in 2023.
Let e intelligence help you evaluate whether Google AMP is still relevant for your website in 2023 and explore other options for improving mobile user experience and search engine visibility.
What is Google AMP?
Google AMP is an open-source framework that enables websites to create fast-loading pages. News sites and blogs often use it, but it can be used by any website that wants to improve its mobile performance.
AMP webpages are displayed with a lightning icon in Google search results, and they load almost instantly. This near-instant loading speed minimizes disruption for users and can help to increase visibility and click-through rates. AMP also has built-in features to support website monetization.
One of these is AMP Ads, which are ads that load up to five times faster than standard Google ads. Another is AMP Stories, which are similar to Facebook, Instagram, and Snapchat stories. These allow users to swipe up on a mobile device to view an entire web page, which will instantly load and earn the publisher a pageview.
Many major online publishers, including The New York Times, eBay, and AliExpress, also use AMP. It is especially popular with news sites, as it allows them to appear in Google’s Top Stories carousel on mobile search results.
How does Google AMP work?
AMP-built pages appear in Google search results with a lightning bolt icon and are cached for faster rendering. It also allows ad networks to deliver ads on AMP-built web pages. They have strict restrictions on HTML/CSS and JavaScript to ensure quick page load times.
AMP pages prioritize the parts of a page that are most important to users using static layouts. For example, it will download images and content likely to be visible below the fold before it starts downloading other pages’ elements. This makes it feel like everything loads simultaneously without jittering, which is a big deal to mobile users.
Another benefit of AMP is that it keeps visitors onsite longer. According to Unbounce, 70 percent of consumers said that when a website loads slowly, they are less willing to buy from it. This can lead to a higher conversion rate for ecommerce sites.
AMP makes pages load faster, so visitors spend more time on the site and are more likely to convert. The AMP format also allows publishers to increase opportunities for ad placements. In addition, AMP pages use less data, which is especially important for mobile users with limited internet access.
In addition, Google gives AMP pages an advantage in search rankings. This is because AMP pages are pre-rendered and cached by Google, which means that the AMP version of a page will appear in search results before the regular HTML page.
Some major publishers have enabled AMP to take advantage of this advantage. These include The New York Times, eBay, and AliExpress. Additionally, AMP pages can be displayed with a special lightning bolt icon on Google Search on mobile devices. This feature makes it easier for visitors to identify AMP pages and decide whether to click on them. However, the benefit of AMP & SEO may be reduced as more sites implement AMP.
Work with e intelligence to optimize your website for mobile users and improve your search engine rankings. Our experts can help you implement AMP and other mobile-friendly SEO solutions.
The Two Factors of Google AMP
Google AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages) has two primary factors that affect its functionality and performance. These are:
AMP HTML
AMP HTML is a stripped-down version designed to improve web page performance on mobile devices. It includes a limited set of HTML tags and properties optimized for speed and efficiency.
AMP HTML also has some additional requirements that are not present in standard HTML, such as:
- All CSS must be inline.
- All images and video tags must have specified dimensions.
- All external resources, such as images and videos, must be loaded asynchronously to prevent blocking of the page load.
AMP JavaScript
AMP JavaScript is a subset of JavaScript designed to optimize the performance of web pages on mobile devices. It provides a streamlined version of JavaScript that prioritizes speed and efficiency over advanced functionality.
AMP JavaScript has some unique characteristics, such as:
- It is loaded asynchronously to prevent blocking of the page load.
- It has limited features and APIs to ensure that scripts do not slow down the page load.
- It enforces strict rules to ensure that scripts do not manipulate the layout of the page, which can cause performance issues.
By using AMP HTML and AMP JavaScript, developers can create fast, efficient, and user-friendly web pages that provide an improved browsing experience for mobile users.
The Pros and Cons of Google AMP
Here are some of the pros and cons of using Google AMP:
Pros:

1. Improved Page Speed: Google AMP pages are light and fast, which is great for mobile users who often have slow or unstable connections. The pages also use less data, which is helpful if you’re using a mobile plan with limited data. AMP pages are designed to load faster and provide a better user experience for mobile users. AMP pages can load in under a second by minimizing the size of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files and prioritizing critical content.
2. Higher Search Rankings: Another pro of AMP is that it can improve page performance, a confirmed ranking factor for Google. Google has indicated that AMP pages may receive a ranking boost in search results, especially in mobile search results. This can lead to increased visibility and traffic for publishers. This makes AMP a good option for blogs and other content sites that want to boost their mobile search rankings.
3. Better User Experience: AMP pages are optimized so that the most important components are loaded first, and ads are only downloaded if necessary. Faster page load times and smoother scrolling can improve the user experience, reducing bounce rates and increasing engagement.
4. Reduced Server Load: AMP pages are cached on Google servers, reducing the load on the publisher’s server and potentially reducing hosting costs.
5. Open Source: AMP is an open-source project, meaning anyone can contribute to its development and use it for free.
Cons:
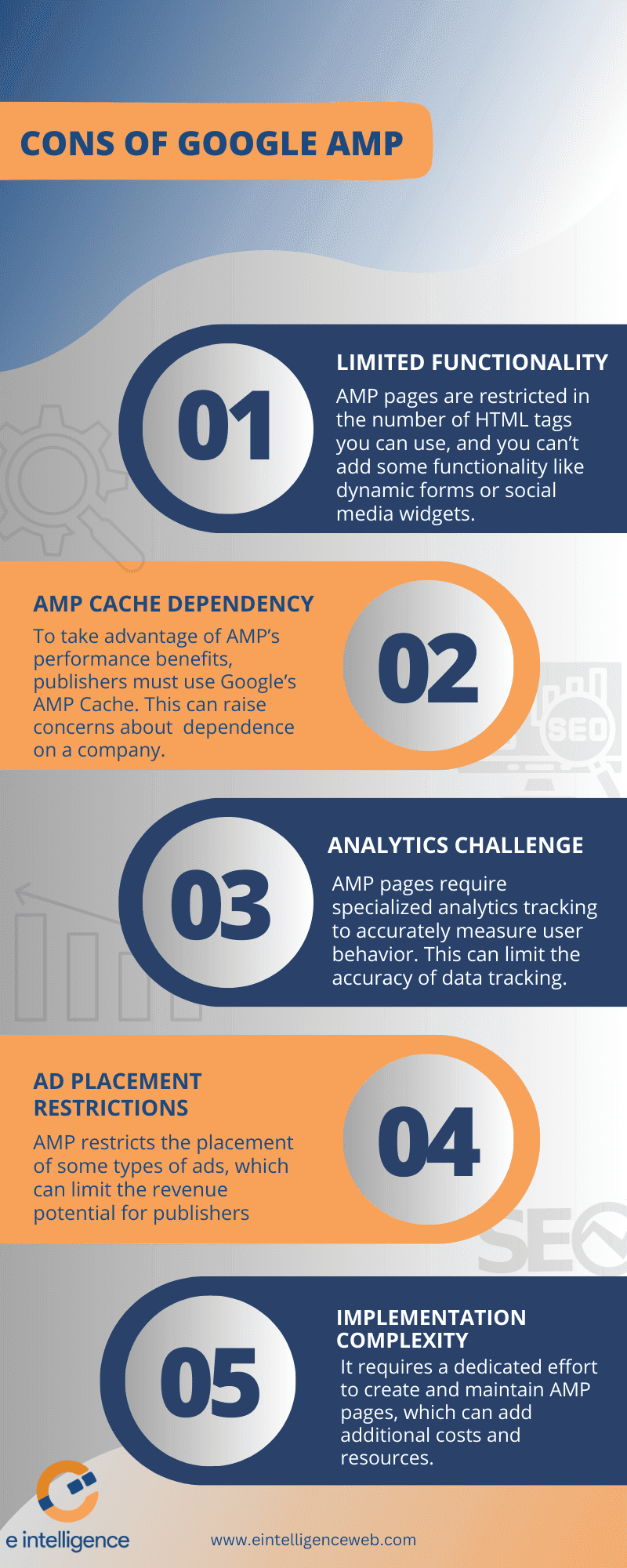
1. Limited Functionality: On the other hand, AMP also has its drawbacks. For one, it can limit your creative freedom. AMP pages are restricted in the number of HTML tags you can use, and you can’t add some functionality like dynamic forms or social media widgets. This can be a problem for some websites, especially for brands or other pages with more complex designs, which may impact the user experience.
2. AMP Cache Dependency: To take full advantage of AMP’s performance benefits, publishers must use Google’s AMP Cache. This can raise concerns about data ownership and dependence on a single company.
3. Analytics Challenges: AMP pages require specialized analytics tracking to accurately measure user behavior. This can add complexity and potentially limit the accuracy of data tracking.
4. Ad Placement Restrictions: AMP restricts the placement of some types of ads, which can limit the revenue potential for publishers. Also, AMP can’t support some types of monetization, including native ads and some third-party analytics platforms.
5. Implementation Complexity: Implementing AMP can be complex, especially for large websites with many pages. It requires a dedicated effort to create and maintain AMP pages, which can add additional costs and resources.
Overall, Google AMP can significantly benefit publishers by prioritizing mobile user experience and search engine visibility. However, the limitations and implementation challenges may not be suitable for all publishers, especially those who require more advanced functionality and customization options.
Contact e intelligence today to learn more about how our digital marketing experts can help you stay up to date on the latest mobile website optimization strategies and technologies.
Does Google AMP Affect SEO Ranking?
AMP pages are a light version of HTML and are crawled and indexed like any other page. Google has explicitly stated that AMP is not a ranking signal and does not give pages a boost in search results. However, many SEO professionals have been skeptical of AMP since its launch. They argue that it is not a fair competition against other websites with fast pages and gives Google too much power over the web.
In addition, AMP has been met with some resistance from publishers, who believe forcing them to use this technology is unfair. For example, some publishers have complained that they cannot get into Google’s story panels for news searches if they do not have an AMP version of their website. Others have reported that AMP pages are not as user-friendly as regular pages and lack features like forms and analytics. Google is aware of these issues and has been working to improve Google AMP in 2023. The bottom line is that AMP is not going away anytime soon, and it is a great option for publishers who want to optimize their mobile content.
How to implement AMP?
Google AMP is a mobile-optimized version of your website. It strips away many elements that make websites slow to load, making them much faster. Most major browsers and platforms support the AMP HTML format, and it can be implemented similarly to regular HTML pages.
To implement Google AMP, follow these general steps:
1. Identify the pages you want to create AMP versions of: Identify the pages on your website that you want to create AMP versions for. Typically, these pages receive a lot of traffic from mobile users, such as blog posts, news articles, and product pages.
2. Create AMP versions of your pages: Create AMP versions of your pages using AMP HTML and AMP JavaScript. You can create AMP versions manually or by using an AMP framework, such as AMP Project or AMP Start.
3. Validate your AMP pages: Validate your AMP pages to ensure they comply with the AMP HTML and AMP JavaScript specifications. You can use the AMP validator to check for errors and warnings.
4. Set up Google AMP Cache: Set up Google AMP Cache to improve the performance of your AMP pages. You can use the default Google AMP Cache or set up your own AMP Cache.
5. Link to your AMP pages: Link to your AMP pages from your main website using rel=”amphtml” in the HTML tag of your main pages. This tells search engines that you have an AMP version of your page.
6. Monitor and optimize: Monitor the performance of your AMP pages and optimize them for speed and user experience. Use AMP analytics to track user behavior and make data-driven decisions.
It’s important to note that implementing AMP can be complex, especially for larger websites with many pages. Additionally, depending on their specific needs and priorities, AMP may not be suitable for all websites. Consider starting with a small number of pages and gradually expanding your AMP implementation as needed.
AMP is designed to work across all devices and web views, which makes it an attractive option for news sites that need to provide an instant-read experience for their readers. Google prioritizes AMP content in search results and shows AMP articles in dedicated carousels in newsy search queries.
However, the benefits of AMP come with some drawbacks. One of the most significant is that it prevents you from using third-party JavaScript, which limits your analytics capabilities and tracking options. Additionally, AMP pages use a cached version of your page, which means that Google Analytics doesn’t monitor user visits unless you make specific adjustments and add unique tracking codes to your AMP pages. This can be a big disadvantage for some site owners.
Get a free website audit from e intelligence to assess the current state of your mobile website and identify areas for improvement.
Current Status of Google AMP in 2023
The AMP project was initially met with skepticism. Many believed it was simply a way for Google to compete with Facebook Instant Articles and Apple News. Others were concerned that the restrictions placed on AMP web pages would reduce user experience. Some were also concerned that AMP pages were being given preferential treatment in search results.
While AMP has improved over time, there are still some issues with the framework. For example, AMP does not support many features available on non-AMP pages, including video and e-commerce. This can lead to a poor user experience, especially on mobile devices.
Additionally, AMP pages are not fully SEO-friendly. They do not use canonical tags, which can cause duplicate content issues. They also do not support standard analytics tags, making it difficult to track the performance of AMP pages. Finally, AMP limits the number of ad formats that can be used on websites, which can impact advertising revenues. Despite these issues, AMP is still a popular option for publishers who want to create fast-loading, lightweight pages.
Technical Limitations of Google AMP
Several technical limitations to AMP should be noted. The most important limit is that AMP pages are loaded from Google’s servers, which can significantly affect performance. Additionally, AMP pages do not support some popular features, such as web forms and social media sharing buttons.
Finally, AMP limits the use of third-party JavaScript, which can limit the functionality of some websites. This can be a problem for e-commerce sites, which rely on JavaScript to collect visitor information and place orders.
While the AMP project has shortcomings, it is still a valuable tool for improving mobile website speed. It has helped many businesses increase their engagement with users and improve their search engine optimization (SEO). If you have a slow-loading mobile website, it is worth considering the pros and cons of AMP. However, if you have a fast-loading mobile site, there is no need to implement AMP. Instead, you should focus on mobile-friendly SEO best practices. This will ensure that your website is ranking well in mobile search results.
Follow e intelligence on social media and subscribe to our blog to stay informed about the latest trends and insights in digital marketing and SEO services.
Google AMP Best Practices
Accelerated mobile pages (AMP) are stripped-down versions of web pages that load faster on mobile devices. They work best for visitors with less-stable Internet connections and increase click-through rates on ads.
Google AMP is an open-source technology that allows pages to load almost instantly on mobile devices. It is also a great way to optimize for speed, which is now one of the most important SEO factors. However, there are some things that you should keep in mind before implementing AMP on your site.
1. Follow AMP HTML Guidelines
Essentially, AMP pages will appear almost identical to your standard web pages but with a lightning bolt icon next to them in Google search results. If you have both AMP and non-AMP pages on your site, it’s important to make sure you canonicalize them correctly so that Google doesn’t penalize you for duplicate content.
Use valid AMP HTML and ensure that your AMP pages pass the AMP validation test. This involves linking to the non-AMP version of a page with a rel=”canonical” tag. AMP also has its markup language that allows you to add information such as title tags and meta descriptions. It can be used to improve the visibility of your AMP pages in search results and can also help with third-party tools that are used for lead capturing and audience tracking.
2. Use AMP Cache
AMP’s light-weight HTML, limited JavaScript and CSS, and caching and preloading on Google’s servers make pages load almost instantly. This is important for mobile users with less-stable internet connections and helps boost search engine rankings, as page speed is now a ranking factor.
The AMP Cache provides a layer of security that ensures validation at the last stage of pre-rendering, meaning that malicious actors can’t spoof AMP pages. Additionally, AMP supports a large number of analytics providers to ensure that traffic is properly attributed.
This also means that if you change something on your website, the AMP version of your site will be cached and displayed to visitors until it is updated on your server. Luckily, there is an API that allows you to flush the cache and force a new copy to be stored on Google’s servers. Then, when you refresh your browser, the latest AMP URL will display in place of the old one. This makes it easy for your readers to update their bookmarks and RSS feeds.
3. Optimize Images
Images are one of the biggest factors that affect page load time. It’s important to optimize them to ensure that your website loads quickly. Search engines give negative marks to websites that load slowly.
Optimizing your images is an easy way to improve your website’s speed and performance. Large, unoptimized photos can make your site slow and clunky. Users don’t want to wait for a slow site, so they leave it before it loads.
AMP uses the GPU, or graphics processor, to accelerate image rendering. This can significantly improve loading times. It also shifts some work from the CPU, freeing up the processor to do other tasks.
It’s important to use high-quality images on your AMP pages. This will ensure that your site looks great and is more attractive to potential customers. It’s also important to size your images correctly. Ensure they are the right size and file format for your AMP page. This will help your website load faster and make it easier for visitors to interact with your content.
4. Minimize CSS and JavaScript
AMP uses a streamlined version of CSS that reduces page size and website bandwidth usage. It also defers JS and CSS loading, which makes the site faster. However, this can create some issues for certain websites. For example, ensuring that all AMP-compatible forms are properly configured is important. This includes enabling async processing and declaring image heights and widths.
AMP requires all styles to be inline and limited to 50 KB, which reduces the number of HTTP requests that must be made for page layout. It also limits the use of JavaScript and only allows asynchronous scripts. This prevents the delay caused by non-async scripts that block DOM construction and affect page rendering time. This approach also helps make AMP pages responsive to changes in browser size.
5. Implement Lazy Loading
When it comes to AMP, Google’s goal is to provide better mobile user experiences. This includes faster loading times and reduced bounce rates. It also aims to keep users on the web rather than in apps.
AMP pages must be designed and built differently from their canonical counterparts to achieve these goals. However, monetization elements like social media sharing icons, related content, login forms, and ads should function the same on AMP pages as on canonical ones.
Lazy loading can help with this. The idea is that certain elements will only be loaded when they are within the viewport, which makes the page load much faster. This can be achieved by using placeholder content and empty containers, which are not downloaded until the user is in view of them.
Lazy loading is especially important for AMP ads, which are rendered on top of the DOM and can be delayed until they are in view. This can significantly improve ad viewability and revenue for publishers who adopt it.
6. Avoid Third-Party JavaScript
With Google moving to a mobile-first index, many website owners are looking at ways of improving their site’s load speed. One way of doing this is to use AMP. The AMP framework allows websites to have fast-loading pages by replacing HTML tags with their versions. This reduces the amount of data that needs to be downloaded and improves page performance.
AMP also uses CSS and JavaScript asynchronously to create a smooth user experience. This improves the loading times of pages and makes them more responsive. However, some third-party scripts are vulnerable to XSS attacks and can be used for malicious purposes. This can lead to a malicious website gaining access to sensitive information.
To avoid this, it’s important to only use trusted third-party scripts. Another option is to defer the load on JavaScript by using a library like pre-connect or DNS-prefetch. This can shave up to 3 seconds off the time it takes for a webpage to become visually complete. However, it’s essential to test this extensively before implementing it.
7. Use AMP Analytics
AMP is a mobile-optimized version of web pages that eliminates many clunky desktop elements that slow down page load times. By reducing loading times, Google aims to make users stay onsite and search longer to find what they’re looking for.
As a bonus, AMP can increase your visibility in search results. AMP with valid structured data makes it more likely to appear in the top stories carousel or have rich result features (such as a headline and larger-than-thumbnail image).
However, since AMP removes a lot of analytics functionality, you’ll need to double-check that your tracking and conversion integrations are working correctly. For example, if you use Google Analytics, be sure to utilize client IDs and unify sessions across AMP and non-AMP pages. You’ll also want to ensure that any AMP-specific tracking, such as trackPageView, is firing as expected. You can enable AMP analytics using the amp-analytics> tag in your head section. Specify the data you want to collect and send to your analytics server in the JSON configuration object.
8. Get Professional Help
The AMP format is especially useful for news sites and e-commerce organizations, who can take advantage of the AMP Top Stories carousel to promote their content. However, the AMP design limitations can make it challenging to build an AMP page for an SEO-optimized website. The lack of customization options can also create inconsistencies between the AMP and canonical versions of a page, which can negatively impact search visibility.
If you are considering using AMP for your website, getting professional help is important. SEO services with AMP experience can guide you through the process and recommend best practices to maximize SEO benefits. They can also help you determine if an AMP version of your page is necessary or if there are other ways to increase mobile conversion rates without sacrificing speed and performance.
With mobile users demanding instant results, optimizing your site for mobile conversions is crucial. A fast-loading website will improve user experience and encourage people to complete key actions, such as filling out a form or making a purchase. It’s important to remember that mobile conversion rate optimization is a constant process, so don’t forget to test and optimize your pages regularly. A reputable SEO agency like e intelligence can help you create AMP webpages that meet all the requirements for a great mobile experience and a high ranking on Google SERPs.
9. Optimize For Mobile Devices
Google’s AMP project is designed to speed up mobile websites and provide a better user experience. Studies have shown that 53% of mobile visitors will abandon a website if it takes more than three seconds to load. In addition, a recent survey by Unbounce found that mobile users spend an average of 19% more time on mobile-optimized sites.
Optimizing your website for mobile is vital to growing your business. AMP is an excellent solution for mobile conversion rate optimization (CRO), but it’s not the only way to improve your website performance and user experience.
Gizmodo, a technology blog, began using AMP in 2016. Their AMP pages load nearly instantly on all devices and have been ranked higher in mobile search results. They achieved this by reducing the number of JavaScript and CSS payloads, adding lazy loading for below-the-fold page elements, and setting a fallback font.
However, while AMP can help with many aspects of CRO, it does not affect core ranking factors such as page load speed. As a result, it’s important to use AMP in combination with other tools and best practices to achieve the best results. One such tool is Google Analytics AMP Support, which provides additional data and insights into how AMP pages perform on mobile devices.
10. Don’t Use AMP on Your Conversion Pages
It’s not uncommon to see websites using AMP to improve the overall load time of their web pages. A report by Unbounce found that when a website’s load time is slow, 45 percent of visitors will leave before they can make a purchase decision. This is why focusing on delivering a fast experience is important, especially for your conversion pages. However, if your web page is a conversion page like your homepage or product landing page, it’s best to skip the AMP version of that page.
The AMP platform strips out certain elements like embedding a Twitter feed, fields for collecting leads, and links to other relevant content on your site. This limits your ability to drive traffic to other pages and removes the possibility of social sharing. AMP also makes it difficult to use standard analytics tags, which can hurt your SEO-optimized website.
11. Implement Structured Data
Google wants to make search more intelligent and understandable for its users. It does this by introducing structured data that allows it to better categorize and display content on SERPs. Structured data markup can benefit businesses by making their products and services more visible to potential customers.
It also makes integrating social media and other third-party platforms into your website easier without sending the user away from your domain. That leads to fewer lost sales and a more seamless customer experience.
As such, it’s important to implement structured data on all web pages. The easiest way to do this is by using Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper tool. This allows you to enter the type of information you want to be marked up and then generates a script to do so.
Note that it’s important to only add structured data relevant to the page you’re marking up. Google has strict guidelines for this and will penalize sites that violate them. Additionally, it’s best to focus on the item types most likely to provide value to your customers.
12. Use Regular A/B Testing and Optimize
In digital marketing, conversions are defined as any action a visitor takes on your website that leads to a desired outcome (such as downloading an eBook, signing up for your email newsletter, or making a purchase). Because mobile users are more likely to complete a conversion, optimizing your site’s mobile experience is an important part of CRO. One way to do this is through regular A/B testing and optimization.
AMP allows you to add A/B testing snippets to your pages that will track the performance of different page versions. This helps you see what changes are most impacting your performance and how well your current strategy is working for your business. It also gives you the information you need to make any necessary adjustments.
Sign up for a consultation with e intelligence to discuss your specific needs and priorities for mobile website optimization and develop a customized strategy for success.
Conclusion
Google AMP has become a popular solution for publishers looking to optimize their mobile content. The technology can dramatically reduce load times on mobile devices and increase page speed, a major ranking factor for search engines. However, it comes with some drawbacks that you should be aware of before implementing it on your conversion pages.
The AMP format prioritizes efficiency over user experience, so it may not be the right option for publishers that want to include rich media content or dynamically-populated components on their pages. AMP also limits the number of advertisements that can appear on a page and does not support disruptive ads like expandables. In addition, if you choose to use the AMP HTML for your pages, Google requires that you canonicalize them back to a non-AMP version of your page. This is to prevent duplicate content from being flagged by Google.
In conclusion, Google AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages) has been an important development in mobile website optimization since its introduction in 2015. It has helped to improve the speed and user experience of mobile websites while also providing a potential boost in search engine rankings.
However, as we move into 2023, the relevance of Google AMP may be a topic of debate. The need for fast and mobile-friendly websites is still important, and AMP can help to achieve this. On the other hand, advances in web technologies and mobile device capabilities may make AMP less necessary or even obsolete in some cases.
Ultimately, whether or not Google AMP is still relevant in 2023 will depend on various factors, including the specific needs and priorities of individual websites and businesses. It may be worth considering whether implementing AMP is worth the investment of time and resources and whether it aligns with broader digital marketing and SEO services.
Overall, while Google AMP may not be the only solution for mobile website optimization, it can still benefit those who prioritize mobile user experience and search engine visibility. As technology continues to evolve, it will be important to stay current on the latest developments and make informed decisions about the best approaches to mobile website optimization.
Join the growing list of satisfied clients who have improved their mobile website performance with e intelligence. Contact us today to learn more about our AMP & SEO services and how we can help you achieve your goals.